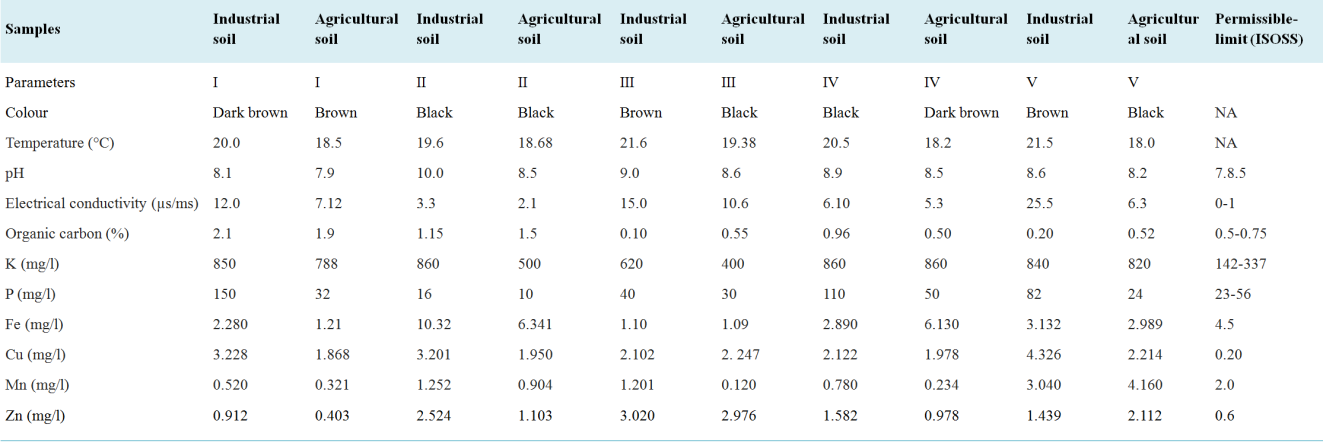
The presence of untreated textile effluents is a significant problem in urban areas. In the absence of treatment, complicated effluent that contains a number of colors, metallic pollutants, and a variety of organic chemicals that are necessary for softeing, printing, and heat stabilization can accumulate in natural sources, leaching into water and soil, and so deteriorating the quality of the soil. The primary purpose of this investigation is to investigate the influence that textile effluent has on the physicochemical characteristics of soil. The inquiry required the collection of soil samples from five different locations, each of which housed a textile dyeing business. A wide range of physicochemical characteristics, such as pH, electrical conductivity, cation exchange capacity, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, organic carbon percentage, acidity, moisture content, micronutrients (Fe, Cu, Mn, Zn), and SAR values, are evaluated in order to determine the quality of the soil. In the process of penetrating the food web, the high concentration of pollutants in the soil reduces the fertility and quality of the soil. It is of the utmost importance to take into account their direct or indirect impact on humankind. By monitoring many physicochemical parameters of polluted textile industry soil and comparing them with agricultural soil samples, the purpose of this study is to evaluate the impact that textile industries have on the quality of the soil in the Hamirgarh and Mandal RIICO industrial regions of Bhilwara.
| Published in | Industrial Engineering (Volume 9, Issue 1) |
| DOI | 10.11648/j.ie.20250901.11 |
| Page(s) | 1-8 |
| Creative Commons |
This is an Open Access article, distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, provided the original work is properly cited. |
| Copyright |
Copyright © The Author(s), 2025. Published by Science Publishing Group |
Heavy Metal, Sar, Dyeing Industry, Soil Qualities
AAS | Atomic Adsorption Spectrophotometer |
SAR | Specific Absorption Ratio |
COD | Chemical Oxygen Demand |
ISOSS | Indian Society of Soil Science's Permitted Standard |
EC | Electrical Conductance |
OC | Organic Carbon |
| [1] | Markandeya, D. Mohan, and S. P. Shukla, “Hazardous consequences of textile mill effluents on soil and their remediation approaches,” journal Cleaner Engineering and Technology vol. 7, pp 100434, 2022. |
| [2] | P. K. Bharti, and C. Awnish, “Soil quality and contamination”, Discovery Publishing House, Delhi, pp 186, 2013. |
| [3] | S. Sumithra, and C. Ankalaiah, J. D. Rao, R. T. Yamuna, “Case study of physicochemical characterization of soil around the industrial and agricultural area of Yerraguntla, Kadapa District, A. P, India. Int. J. of Geology, Earth & Environmental Sciences, vol. 3, pp 8-34, 2013. |
| [4] | S. K. Bajpai, et al., “Seasonal Analysis of Soil Sediment of Shahpura Lake of Bhopal”, International Journal of Environmental Science and Development, vol. 1, no. 4, 2010. |
| [5] | F. Degryse et al., “Soil management and fertilizer practices affecting crop production and human health. In The Nexus of Soils, Plants, Animals, and Human Health”, Stuttgart, Germany: Schweizerbart, pp. 111-121, 2017. |
| [6] | C. Barot. and V. Patel., “Comparative study of seasonal variation in Physicochemical Properties of selected wetlands of Mehsana district, North Gujarat”, Jan. Indian Journal of applied research, vol. 4, no. 7, ISSN- 2249- 555X JULY 2014. |
| [7] | Thesis: Verma, R, “A Chemical Study On Industrial Effluent On Soil and Water Around Bilaspur”, Dr. C. V. Raman University Department of Chemistry, Completed the year 2015. |
| [8] | Sen, P., Mehta, R. & Mehta, P. Water quality assessment of Banas River, eastern-south region of Rajasthan, using water quality index. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. 89, 134–142 (2023). |
| [9] | N. Dhaker, P. Mehta and R. Mehta, Impact of Dying Industrial Effluent on Physicochemical Parameters of Ground Water Quality of Industrial Area of Bhilwara, Rajasthan. Studies in Indian Place-Names. ISSN: 2394- 3114 vol. 40, Issue 68, 2020. |
| [10] | L. Baskaran, et al., “Amelioration of Sugar Mill Effluent Polluted Soil and its Effect on Green gram (Vigna radiate L.)”, Botany Research International, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 131-135, 2009. |
| [11] | N. Dhaker, P. Mehta, and R. Mehta, Impact of Dye Industrialeffluent on Soil Quality Parameters at Rico Industrial Area Bhilwara Rajasthan. Journal Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. Special Issue vol 13 No 10 Pp. 293-296, 2020. |
APA Style
Dhaker, N., Mehta, P., Sen, P., Mehta, R., Bhatt, A. (2025). Impact of Textile Dyeing Effluent on Soil Quality Parameters. Industrial Engineering, 9(1), 1-8. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ie.20250901.11
ACS Style
Dhaker, N.; Mehta, P.; Sen, P.; Mehta, R.; Bhatt, A. Impact of Textile Dyeing Effluent on Soil Quality Parameters. Ind. Eng. 2025, 9(1), 1-8. doi: 10.11648/j.ie.20250901.11
AMA Style
Dhaker N, Mehta P, Sen P, Mehta R, Bhatt A. Impact of Textile Dyeing Effluent on Soil Quality Parameters. Ind Eng. 2025;9(1):1-8. doi: 10.11648/j.ie.20250901.11
@article{10.11648/j.ie.20250901.11,
author = {Nirma Dhaker and Preeti Mehta and Pankaj Sen and Rajeev Mehta and Abhilasha Bhatt},
title = {Impact of Textile Dyeing Effluent on Soil Quality Parameters},
journal = {Industrial Engineering},
volume = {9},
number = {1},
pages = {1-8},
doi = {10.11648/j.ie.20250901.11},
url = {https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ie.20250901.11},
eprint = {https://article.sciencepublishinggroup.com/pdf/10.11648.j.ie.20250901.11},
abstract = {The presence of untreated textile effluents is a significant problem in urban areas. In the absence of treatment, complicated effluent that contains a number of colors, metallic pollutants, and a variety of organic chemicals that are necessary for softeing, printing, and heat stabilization can accumulate in natural sources, leaching into water and soil, and so deteriorating the quality of the soil. The primary purpose of this investigation is to investigate the influence that textile effluent has on the physicochemical characteristics of soil. The inquiry required the collection of soil samples from five different locations, each of which housed a textile dyeing business. A wide range of physicochemical characteristics, such as pH, electrical conductivity, cation exchange capacity, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, organic carbon percentage, acidity, moisture content, micronutrients (Fe, Cu, Mn, Zn), and SAR values, are evaluated in order to determine the quality of the soil. In the process of penetrating the food web, the high concentration of pollutants in the soil reduces the fertility and quality of the soil. It is of the utmost importance to take into account their direct or indirect impact on humankind. By monitoring many physicochemical parameters of polluted textile industry soil and comparing them with agricultural soil samples, the purpose of this study is to evaluate the impact that textile industries have on the quality of the soil in the Hamirgarh and Mandal RIICO industrial regions of Bhilwara.},
year = {2025}
}
TY - JOUR T1 - Impact of Textile Dyeing Effluent on Soil Quality Parameters AU - Nirma Dhaker AU - Preeti Mehta AU - Pankaj Sen AU - Rajeev Mehta AU - Abhilasha Bhatt Y1 - 2025/02/26 PY - 2025 N1 - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ie.20250901.11 DO - 10.11648/j.ie.20250901.11 T2 - Industrial Engineering JF - Industrial Engineering JO - Industrial Engineering SP - 1 EP - 8 PB - Science Publishing Group SN - 2640-1118 UR - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ie.20250901.11 AB - The presence of untreated textile effluents is a significant problem in urban areas. In the absence of treatment, complicated effluent that contains a number of colors, metallic pollutants, and a variety of organic chemicals that are necessary for softeing, printing, and heat stabilization can accumulate in natural sources, leaching into water and soil, and so deteriorating the quality of the soil. The primary purpose of this investigation is to investigate the influence that textile effluent has on the physicochemical characteristics of soil. The inquiry required the collection of soil samples from five different locations, each of which housed a textile dyeing business. A wide range of physicochemical characteristics, such as pH, electrical conductivity, cation exchange capacity, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, organic carbon percentage, acidity, moisture content, micronutrients (Fe, Cu, Mn, Zn), and SAR values, are evaluated in order to determine the quality of the soil. In the process of penetrating the food web, the high concentration of pollutants in the soil reduces the fertility and quality of the soil. It is of the utmost importance to take into account their direct or indirect impact on humankind. By monitoring many physicochemical parameters of polluted textile industry soil and comparing them with agricultural soil samples, the purpose of this study is to evaluate the impact that textile industries have on the quality of the soil in the Hamirgarh and Mandal RIICO industrial regions of Bhilwara. VL - 9 IS - 1 ER -